Briefly Identify and Explain the Different Types of Karst Topography.
Sinkhole cenote limestone shore cave polje mogote foibe Types of Karst karst Landscapes Karst topography geological formation shaped dissolution. Caves and Caverns are common of Karst topography.

Karst An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
When limestone interacts with underground water the water dissolves the limestone to form karst topography - an amalgamation of caves underground channels and a rough and bumpy ground surface.
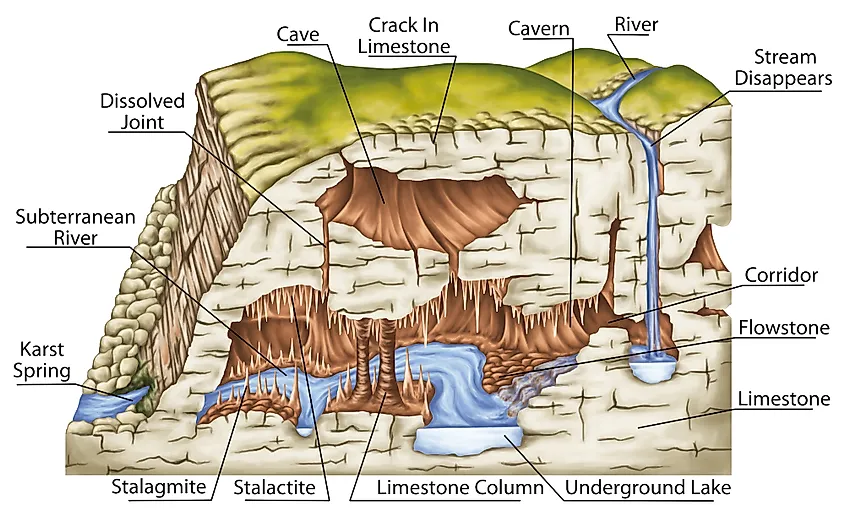
. Karst topography describes the distinct landscape that is made when underlying rocks dissolve or change shape. The subsurface features are the areas of dissolution within the rock. Two or more devices connect to a link.
Karst topography is usually formed when acidic water dissolves layers of. This forms caves fissures underground wells jagged hills cliffs river beds and other types of terrain. Identify various geologic features associated with groundwater.
It is found in regions abundant in limestone dolomite and gypsum. However not all features will be found at all locations. Topographical maps show landforms such as hills and mountains.
Karst is associated with soluble rock types such as limestone marble and gypsum. 56K views View upvotes Jaivardhan Jha. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves.
Distribution of Karst Topography. The term topology in computer networking refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically. Neither 1 nor 2.
In a valley the water often gets lost through cracks and fissures in the bed. Common geophysical methods to be. These are small depressions dotting a karst landscape.
Karst is a type of landscape where the dissolving of the bedrock has created sinkholes sinking streams caves springs and other characteristic features. Karst topography is a is a landscape that is formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks. Look it up now.
The topology of a network is the geometric representation of the relationship of all links and linking devices usually called nodes to one another. Karst topography is named for the Kras plateau region of eastern Italy and western Slovenia Kras is Karst in German for barren land. Besides karst topography also develops on dolomite dolomitic limestones and chalks.
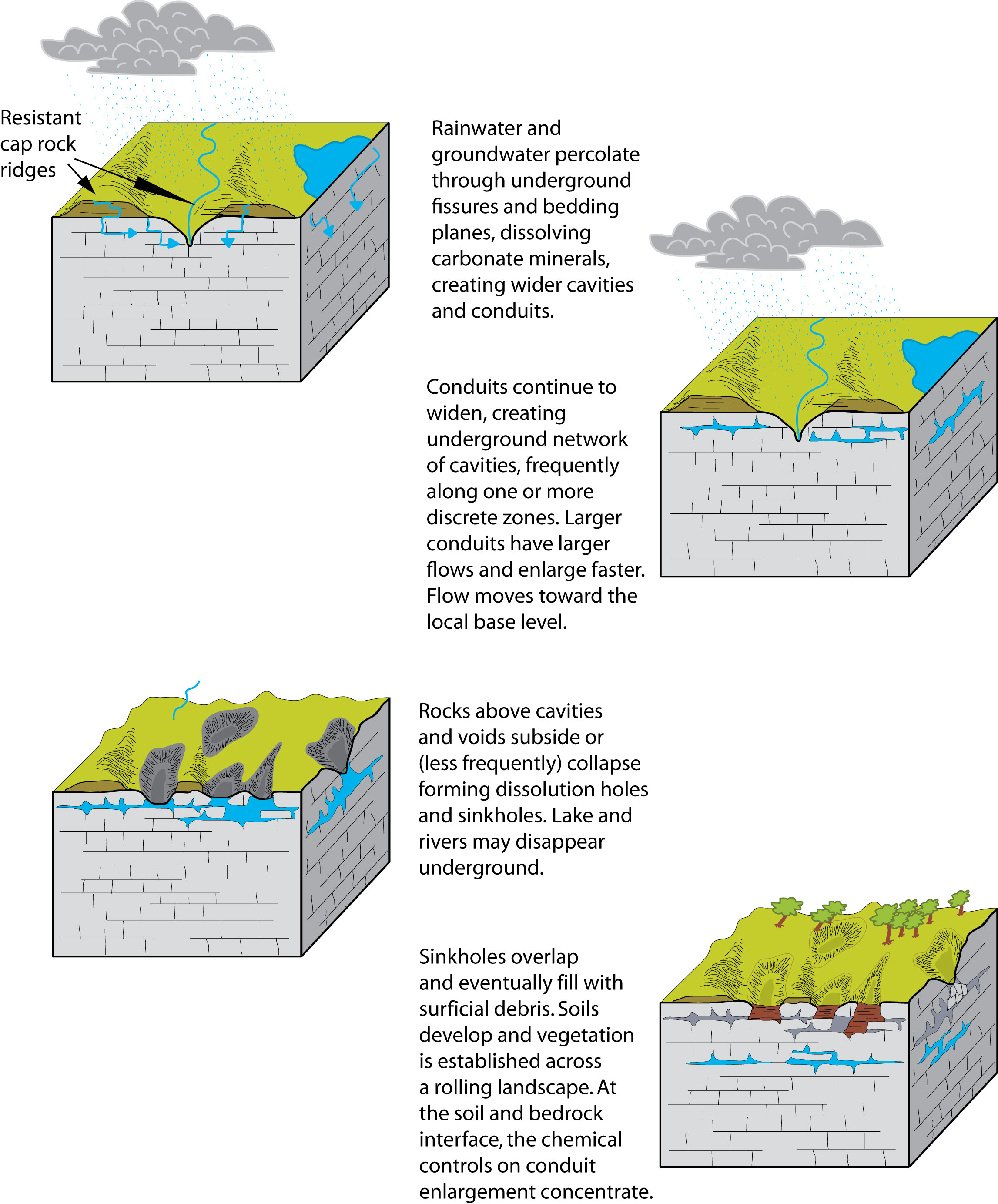
Where relief is slight sinkholes predominate. Karst topography generally forms in areas of abundant rainfall where bedrock comprises of carbonate-rich rock. These are called sinking creeks and if their tops are open they are called bogas.
Let us look at the type of Network Topologies available. Karst topography and landscapes. Karst Topology is formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks including limestone dolomite and gypsum.
Where relief is greater cliffs and steep slopes alternate with streamless valleys. 1 the dissolution of bedrock forming a bowl-shaped depression or 2 the collapse of shallow caves that were formed by. The green shading displays where karst regions are located.
It is characterized by sinkholes caves and underground drainage systems. The surface landforms include sinkholes dolines areas of subsidence sinking streams springs and cave entrances. Karst topography dominated by sinkholes or dolines usually has several distinct surface features.
A map of the United States showing regions displaying or having active karst topography. Karst landscapes develop because of lack of drainage. Both 1 and 2.
Karst topography generally develops in those areas where thick beds of massive limestones lie just below the layer of surficial materials. Data is transmitted in a single route from one point to the other. It is usually associated with sinkholes dollies and caves which are are key examples of drainage systems.
With vertical sides and conical shapes are residual karst features that dominate some parts of the world and are riddled with caves. 18 rows The green regions indicate area with a majority bedrock composition of limestone. In general the types of karst features can be divided into surface landforms and subsurface features.
Karst topography is a landscape formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone dolomite and gypsum. Of the karst-forming rocks the carbonates dolostone and limestone are much more abundant than evaporites mostly deposits of gypsum and anhydrite therefore karst landscapes are most often found in regions underlain by carbonate rocks. C Abundant rainfall carbonate-rich rock caves all are features of karst topography.
This section will discuss some of these features including karst topographywhat it is and where it is located geyserswhat causes them and how they work and springsthe different types of springs and how they work. When a number of adjoining sink holes collapse they form an open broad area called a karst window. Select the correct ones.
Our paper model shows features normally associated with karst topography. Karst requires water circulation it will not usually develop in areas where the water is frozen or little rain falls. Sinkholes also known as dolines are surface depressions formed by either.
Bus topology is the kind of network topology where every node ie. Groundwater and its behavior can produce a variety of common features. A discussion of the methods that are commonly applied to karst investigations the advantages and disadvantages of the methods acquisition parameters and the kinds of results to be expected will be presented.
We cannot transmit data in both ways. Two or more links form a topology. Paper briefly examines geophysical standards that have been developed.
Nearly all surface karst features are formed by internal drainage subsidence and collapse triggered by the development of underlying caves. The red regions indicate areas with active major karst topography. What are features of krast topography.
Some regions of karst topography are dominated by several caves. Besides typical karst region of earstwhile Yugoslavia karst topography has well developed in Causes Region of. Every device on the network is connected to a solo main cable line.
It has also been documented for wethering-resistant rocks such as quartzite given the right conditions.

Karstification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
No comments for "Briefly Identify and Explain the Different Types of Karst Topography."
Post a Comment